
Source: What is Circadian Rhythm? by SleepFoundation.org
Slide

What is Circadian Rhythm?
EFFECT OF BIOLOGICAL CLOCK, ESSENTIAL FUNCTIONS, INFLUENCED BY ENVIRONMENTAL CUES
Lighting
Social Activities
Temperature

Digestive system produce proteins to match the typical timing of meals
Endocrine system regulates hormones to suit normal energy expenditure
Light exposure generate
alertness
Production of melatonin hormone that
promote sleep
Slide
ERGONOMIC CIRCADIAN LIGHTING
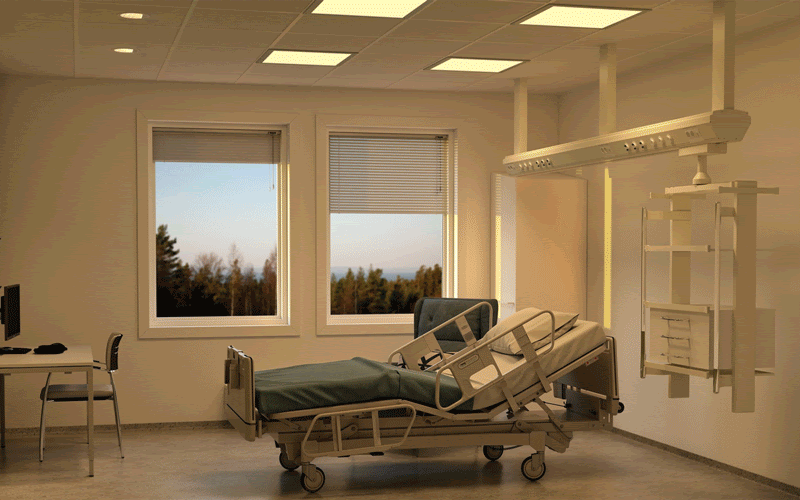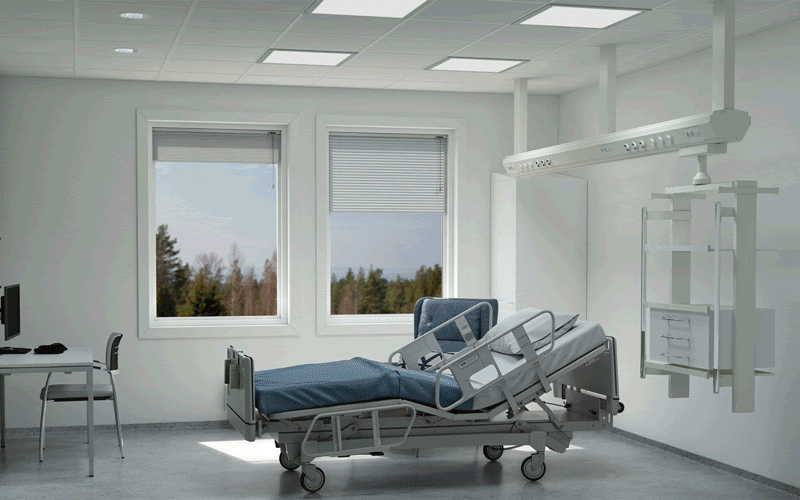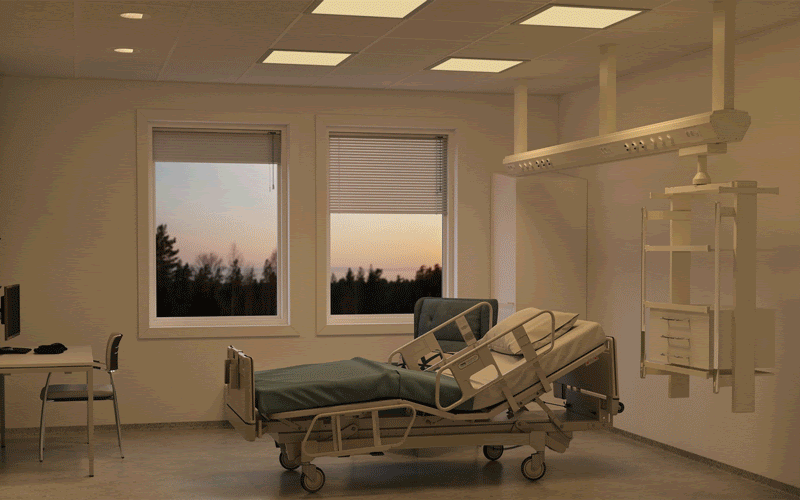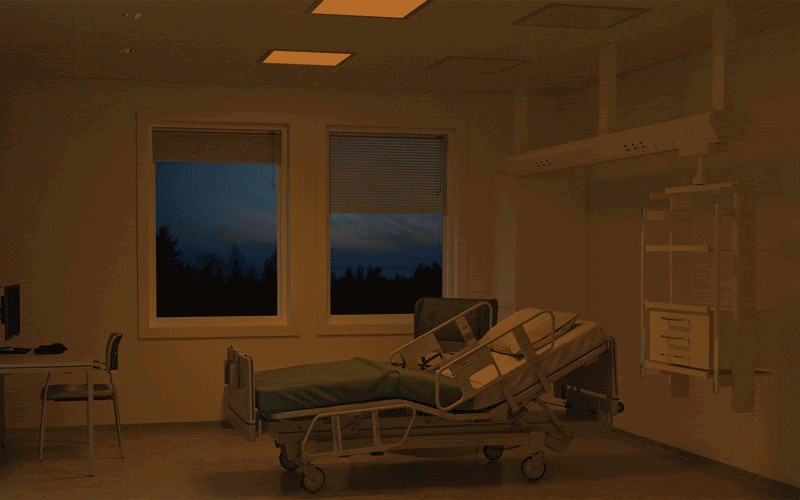


Light not only enables us to see fine detail, colour and motion, but also exerts non-visual effects on circadian rhythms,
sleep and mood.


Light at the wrong time may
disrupt circadian
rhythms and sleep,
but in the form of light therapy, light exposure can be used as an intervention for psychiatric and other medical conditions.
Slide
Circadian Misalignment Effect
REVIEW: LIGHT, SLEEP AND CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS IN OLDER ADULTS WITH ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE AND RELATED DEMENTIAS
- Circadian control of aggression
- Timed light exposure improve nighttime sleep efficiency, increase daytime wakefulness and reduce evening agitation without the adverse effects of pharmacological solutions.

Source: Review on Light, Sleep and circadian Rhythms in Older adults with Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias by Mariana G Figueiro | Reference2
Slide
Circadian Misalignment Effect
MENTALLY AND PHYSICALLY
Without proper signaling from the body’s internal clock
Struggle to fall asleep
Low quality sleep
Health implications
Slide
Risk of psychiatric illnesses like depression and bipolar disorder as well as the potential for neurodegenerative diseases like dementia


Risk of sleep disorder like obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and insomnia through suppressed secretion of melatonin
Influence immune system as well as processes of DNA repair that are involved in preventing cancer.
Affect metabolism and weight through regulation of blood sugar, cholesterol and levels of leptin (hormone that leave people full after a meal)
Risk of cardiovascular disease
Health implications
Low quality sleep
Struggle to fall asleep
Without proper signaling from the body’s internal clock
MENTALLY AND PHYSICALLY
Circadian Misalignment Effect
